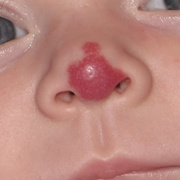
Hemangioma Pictures - 54 Photos & Images
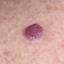
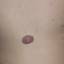
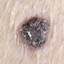
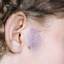
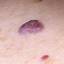
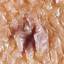
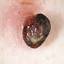
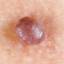
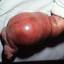
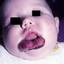
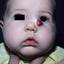
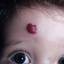
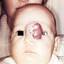
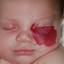
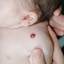
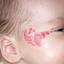
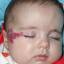
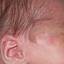
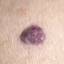
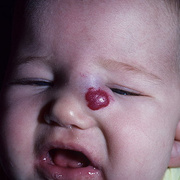
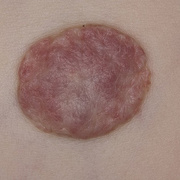
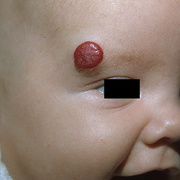
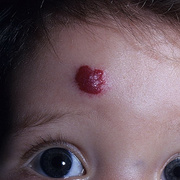
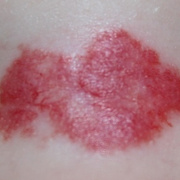
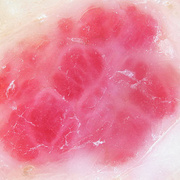
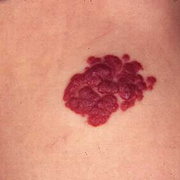
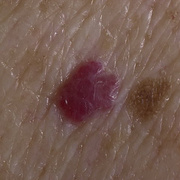
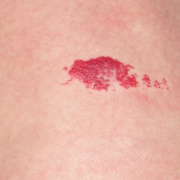
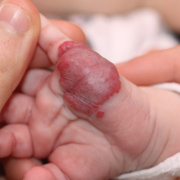
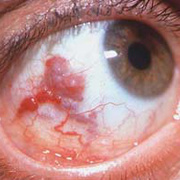
Infantile haemangioma (American spelling ‘hemangioma’) describes a benign (non-cancerous) condition affecting cutaneous blood vessels. It is also known as proliferative haemangioma because it is due to proliferating endothelial cells; these are the cells that line blood vessels. Infantile haemangiomas are proliferative lesions that usually develop shortly after birth. They are distinct from vascular malformations, which are usually present at birth and are less common.
Over 80% of infantile haemangiomas occur on the head and neck area. They grow to 80% of maximum size in the first three months and most stop growing at about 5 months. However, they may keep growing for up to 18 months. After that, they undergo regression or involution. This can take as long as 3-10 years. Nearly all flat infantile haemangiomas eventually involute and disappear without treatment. However, regression of bulky haemangiomas tends to be incomplete, and they may leave an irregular atrophic (thin) scar or anetoderma (a dented scar) in at least 50% of cases.