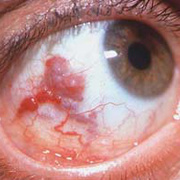
Hemangioma Signs
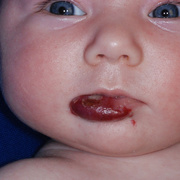
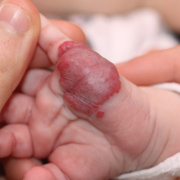
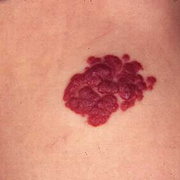
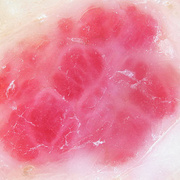
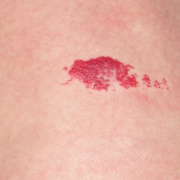
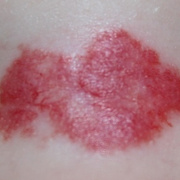
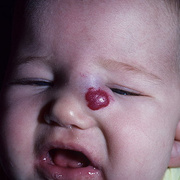
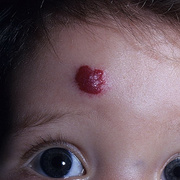
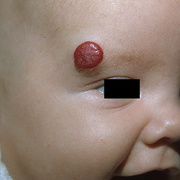
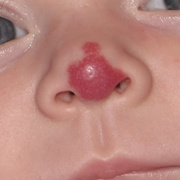
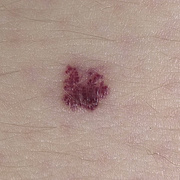
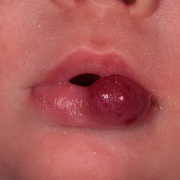
Hemangiomas are noncancerous growths that form due to an abnormal collection of blood vessels. They’re often found on the skin or internal organs, particularly the liver. They are usually congenital, which means that most people develop them before birth, while they’re still in the womb. Hemangiomas on the liver rarely cause symptoms. Usually, they’re not discovered until you are tested for an unrelated condition — this is called an “incidental finding.” Skin hemangiomas appear as small scratches on babies and grow larger as the child ages. However, most hemangiomas of the skin disappear by the age of 10.
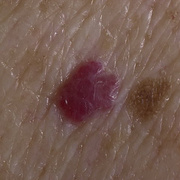
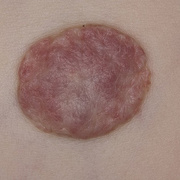
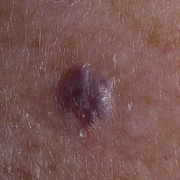
Hemangiomas are usually small, but in some cases they may grow large, or develop lesions and require removal. There are no known ways to prevent the growth of hemangiomas on the skin or organs. How Do Skin Hemangiomas Look? Hemangiomas of the skin usually appear to be small red scratches or bumps. As they grow, their appearance is similar to a burgundy-colored birthmark. Skin hemangiomas are sometimes called strawberry hemangiomas, because of their deep red appearance. This type is mostly found on the neck or the face.
Symptoms of Hemangiomas of the Internal Organs
Hemangiomas inside the body usually go unnoticed until they grow large, or multiple hemangiomas form.
Some symptoms that you might have include:
nausea
vomiting
abdominal discomfort
loss of appetite
unexplained weight loss
a feeling of fullness in the abdomen.