Molluscum Contagiosum on Penis Pictures - 4 Photos & Images
Molluscum contagiosum is an infection caused by a poxvirus (molluscum contagiosum virus). The result of the infection is usually a benign, mild skin disease characterized by lesions (growths) that may appear anywhere on the body. Within 6-12 months, Molluscum contagiosum typically resolves without scarring but may take as long as 4 years.
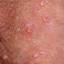
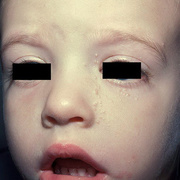
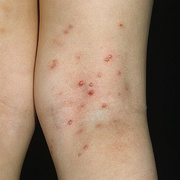
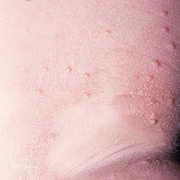
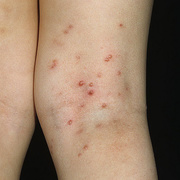
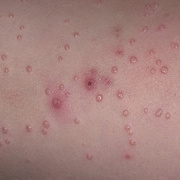
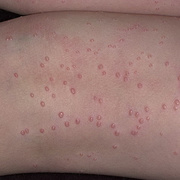
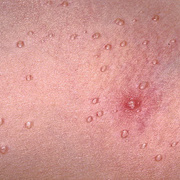
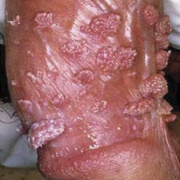
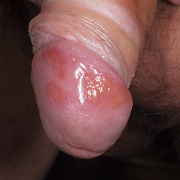
The lesions, known as Mollusca, are small, raised, and usually white, pink, or flesh-colored with a dimple or pit in the center. They often have a pearly appearance. They’re usually smooth and firm. In most people, the lesions range from about the size of a pinhead to as large as a pencil eraser (2 to 5 millimeters in diameter). They may become itchy, sore, red, and/or swollen.
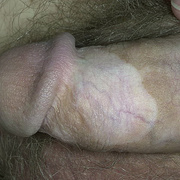
Mollusca may occur anywhere on the body including the face, neck, arms, legs, abdomen, and genital area, alone or in groups. The lesions are rarely found on the palms of the hands or the soles of the feet.
The virus is spread:
- During any type of skin to skin contact such as sexual activity, contact sports, or other activity that involves touching the bumps of an infected person.
- Through contact with a towel, washcloth or something else that has the virus on it.
- To other parts of an infected person’s body by scratching the bumps.
Molluscum contagiosum bumps will usually go away on their own, but it may take several months. Treatment shortens how long you have them. If you have bumps on your genital area such as your penis, inner thighs, buttocks and you’re sexually active; you should be treated to help prevent spreading the virus to your sexual partner(s). Side effects of treatment include: pain, irritation and possible scarring.
For adults who have the small lumps (mollusca) on the skin, a condom should be used during sex. This will not completely stop skin-to-skin spread but will reduce the chance of passing it on considerably.