Chicken Pox Virus Pictures - 36 Photos & Images
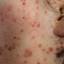
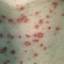
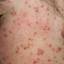
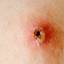
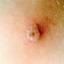
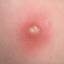
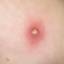
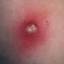
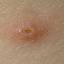
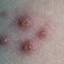
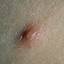
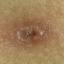
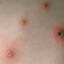
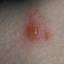
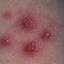
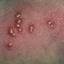
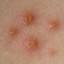
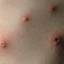
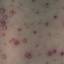
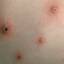
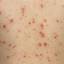
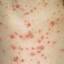
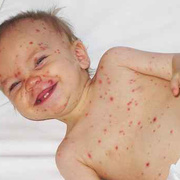
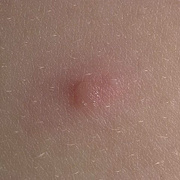
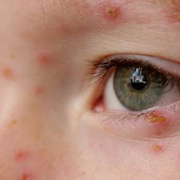
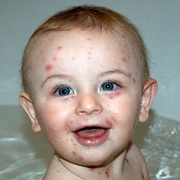
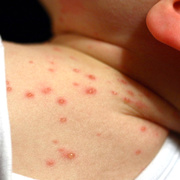
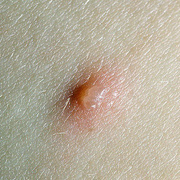
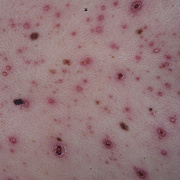
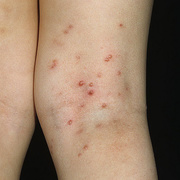
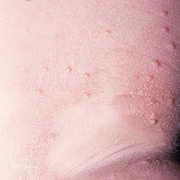
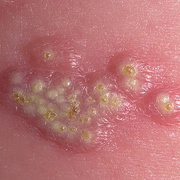
Chickenpox is a highly contagious illness caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV), a type of herpes virus. It is often a mild illness, characterized by an itchy rash on the face, scalp and trunk with pink spots and tiny fluid-filled blisters that dry and become scabs four to five days later. Serious complications, although rare, can occur mainly in infants, adolescents, adults and persons with a weakened immune system. These complications include bacterial infections of skin blisters, pneumonia, and encephalitis (inflammation of the brain). In temperate climates, such as the Northeast, chickenpox occurs most frequently in the late winter and early spring.
Chickenpox is a common childhood illness with 90 percent of the cases occurring in children younger than ten years of age. Before the availability of the varicella vaccine in the U.S., almost everyone developed chickenpox. Most people who are vaccinated will not get chickenpox. Those who are vaccinated and develop chickenpox usually have a mild form of the illness. They have fewer spots and recover faster.
Chickenpox is transmitted from person to person by directly touching the blisters, saliva or mucus of an infected person. The virus can also be transmitted through the air by coughing and sneezing. Chickenpox can be spread indirectly by touching contaminated items freshly soiled, such as clothing, from an infected person. Direct contact with the blisters of a person with shingles can cause chickenpox in a person who has never had chickenpox and has not been vaccinated. Blisters that are dry and crusted are no longer able to spread chickenpox.
Initial symptoms include sudden onset of slight fever and feeling tired and weak. These are soon followed by an itchy blister-like rash. The blisters eventually dry, crust over and form scabs. The blisters tend to be more common on covered than on exposed parts of the body. They may appear on the scalp, armpits, trunk and even on the eyelids and in the mouth. Mild or asymptomatic infections occasionally occur in children. The disease is usually more serious in young infants and adults than in children.
Symptoms commonly appear 14 to 16 days (range of ten to 21 days) after exposure to someone with chickenpox or herpes zoster (shingles).