Eczema Tyloticum Pictures - 60 Photos & Images
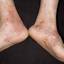
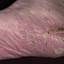
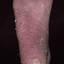
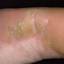
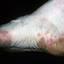
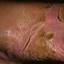
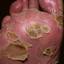
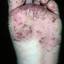
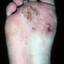
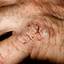
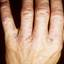
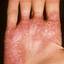
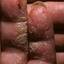
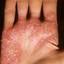
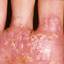
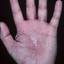
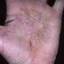
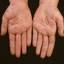
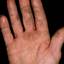
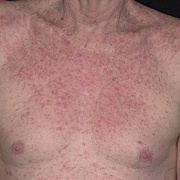
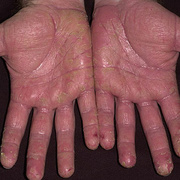
Chronic vesiculosquamous eczema, also called dyshidrotic eczema or eczema tyloticum.
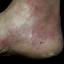
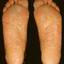
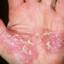
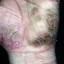
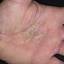
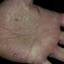
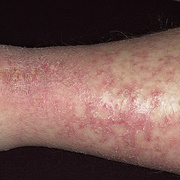
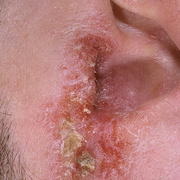
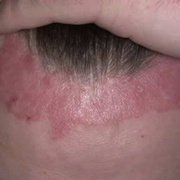
Vesicular palmoplantar eczema is a term used to describe a group of diseases characterized by vesiculobullous eruption involving mainly the hands and feet. Clinical presentations vary from acute dermatitis to more chronic relapsing and remitting disease patterns. The diversity of presentation has created challenges in classifying hand eczema. A 2011 publication assembled an algorithm for chronic hand eczema based on etiology, morphology and clinical features.
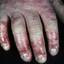
Although considerable overlap exists in the various forms of vesicular palmoplantar eczema, the disease can be roughly divided into four distinct categories: pompholyx, subacute or chronic relapsing vesiculosquamous eczema, chronic vesiculohyperkeratotic or hyperkeratotic eczema, and id reactions.
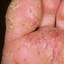
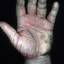
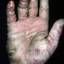
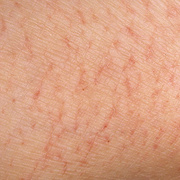
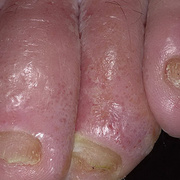
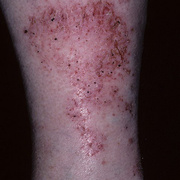
It was initially thought to be caused by abnormal functioning of the sweat glands. This association has since been disproved, but the term dyshidrotic eczema is still used. Patients with this variant present with small (1-2 mm) vesicles on nonerythematous skin involving the inner sides of the fingers or on the palms and soles. The vesicles are pruritic, last 1-2 weeks, desquamate, and then recur at unpredictable intervals.
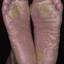
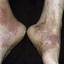
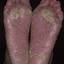
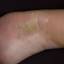
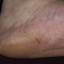
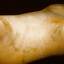
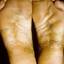
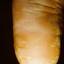
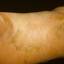
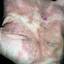
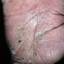
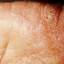
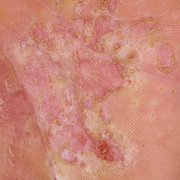
The chronic hyperkeratotic variety involves mainly the central palms, where it causes thickening and fissures. This category is notoriously the most difficult to treat.