What are Symptoms of Chickenpox Pictures - 27 Photos & Images
In immunocompetent children, chickenpox is rarely severe. In adults and immunocompromised children, infection can be serious.
Mild headache, moderate fever, and malaise may occur 10 to 21 days after exposure, about 24 to 36 h before lesions appear. This prodrome is more likely in patients > 10 yr and is usually more severe in adults.
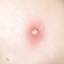
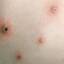
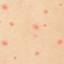
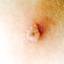
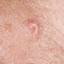
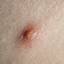
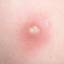
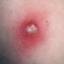
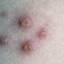
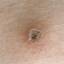
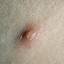
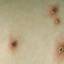
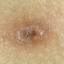
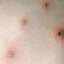
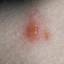
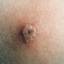
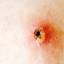
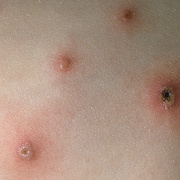
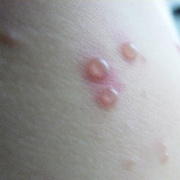
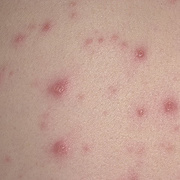
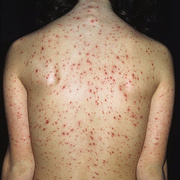
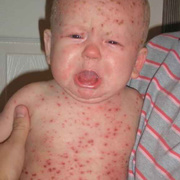
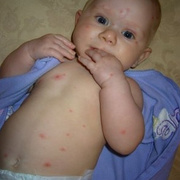
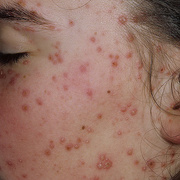
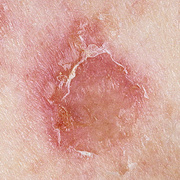
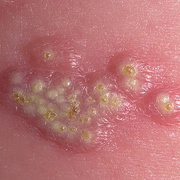
The initial rash, a macular eruption, may be accompanied by an evanescent flush. Within a few hours, lesions progress to papules and then characteristic, sometimes pathognomonic teardrop vesicles, often intensely itchy, on red bases. The lesions become pustular and then crust.
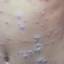
Lesions initially develop on the face and trunk and erupt in successive crops; some macules appear just as earlier crops begin to crust. The eruption may be generalized (in severe cases) or more limited but almost always involves the upper trunk.
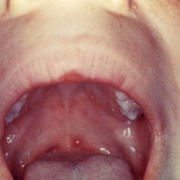
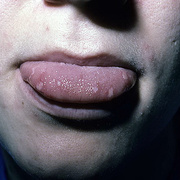
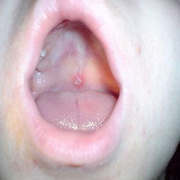
Ulcerated lesions may develop on the mucous membranes, including the oropharynx and upper respiratory tract, palpebral conjunctiva, and rectal and vaginal mucosa.
In the mouth, vesicles rupture immediately, are indistinguishable from those of herpetic gingivostomatitis, and often cause pain during swallowing.
Scalp lesions may result in tender, enlarged suboccipital and posterior cervical lymph nodes.
New lesions usually cease to appear by the 5th day, and the majority are crusted by the 6th day; most crusts disappear <20 days after onset.