Thrombosis Hand Pictures - 7 Photos & Images
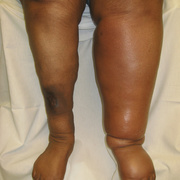
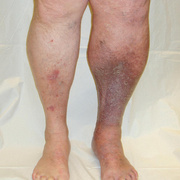
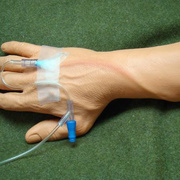
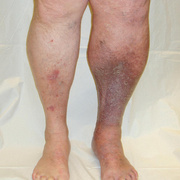
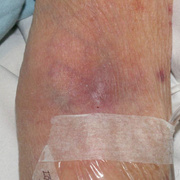
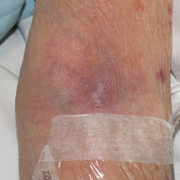
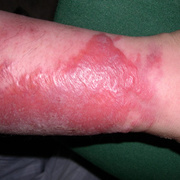
Upper-extremity deep vein thrombosis (UEDVT) is an increasingly important clinical entity with potential for considerable morbidity. Pulmonary embolism (PE) is present in up to one third of patients with UEDVT. Other complications, such as persistent upper-extremity pain and swelling, the superior vena cava (SVC) syndrome, and loss of vascular access, can be disabling and devastating.
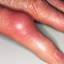
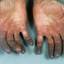
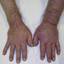
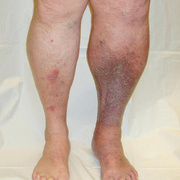
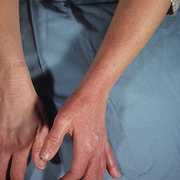
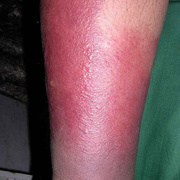
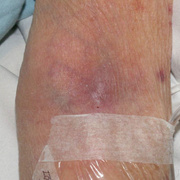
Symptoms of deep vein thrombosis include:
- pain,
- swelling,
- warmth,
- tenderness, and
- redness of the hand.
Axillary or subclavian vein thrombosis may occasionally be completely asymptomatic. More often, though, patients complain of vague shoulder or neck discomfort and arm edema. If thrombosis causes obstruction of the superior vena cava, the patient may complain of arm and facial edema, head fullness, blurred vision, vertigo, or dyspnea.
Patients with thoracic outlet obstruction may have pain that radiates into the fourth and fifth digits via the medial arm and forearm, attributable to injury of the brachial plexus. Symptoms may be position dependent and worsen with hyperabduction of the shoulder or lifting. If thoracic outlet syndrome is suspected, the examiner should palpate the supraclavicular fossa for brachial plexus tenderness, inspect the hand and arm for atrophy, and perform provocative tests, such as Adson’s and Wright’s maneuvers. To perform the Adson test, the examiner extends the patient’s arm on the affected side while the patient extends the neck and rotates the head toward the same side. Weakening of the radial pulse with deep inspiration suggests compression of the subclavian artery. Wright’s maneuver tests for reproduction of symptoms and weakening of the radial pulse when the patient’s shoulder is abducted and the humerus is externally rotated.