Scarlet Fever Signs
Scarlet fever, also known as scarlatina, is an infection that can develop in people who have strep throat. The infection is caused by group A streptococcus bacteria, which are the same bacteria that cause strep throat. These bacteria produce a toxin, or poison, that causes a bright red rash on the body. The scarlet-colored rash is what gives scarlet fever its name. Aside from the rash, people with scarlet fever usually have a high fever and sore throat.
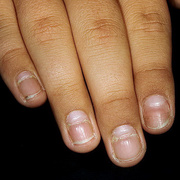
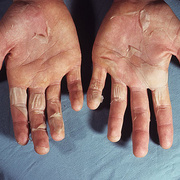
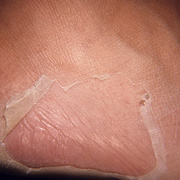
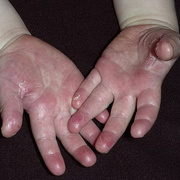
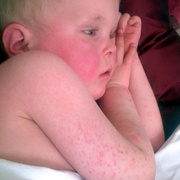
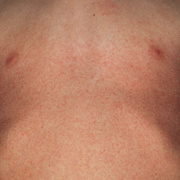
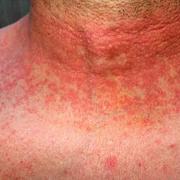
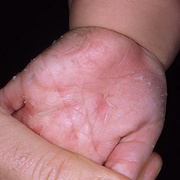
Scarlet fever mainly affects children between ages 5 and 15. It used to be a common and serious childhood illness, but it’s relatively rare today. Antibiotic treatments have reduced the severity of the symptoms and the prevalence of the disease. Researchers aren’t sure why cases of scarlet fever have decreased while cases of strep throat remain common. A rash is the most common sign of scarlet fever. It usually looks like a sunburn and feels like sandpaper. It typically begins on the chest and stomach and then spreads to the rest of your body. The folds of skin around the armpits, elbows, and knees can also become a deeper red than the surrounding rash. The rash typically lasts between two and seven days. After the rash has subsided, the affected skin will peel along with the skin on the tips of the fingers and toes.
Other common symptoms of scarlet fever include:
a fever above 101°F
chills
headaches
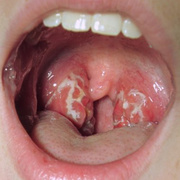
a red, sore throat with white and yellow patches
swollen tonsils
a flushed face
nausea and vomiting
swollen glands in the back of the neck
a pale area of skin around the lips
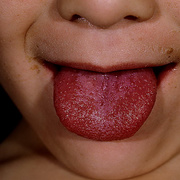
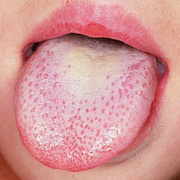
a white tongue with red dots on the surface, which is called strawberry tongue.