Papilloma on the Ears Pictures - 2 Photos & Images
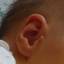
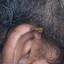
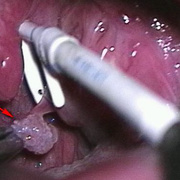
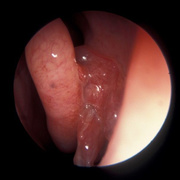
Squamous papillomas are benign tumours which are commonly located in the skin, oral mucosa, upper respiratory tract, upper digestive tract and genital organs and occasionally in the external and middle ear.
Review of literature showed that out of all benign tumours of the ear reported so far, up to 80% are papillomas. More than 90% of these are located in the external auditory canal.
Human papilloma viruses are found to be the main causative agents of squamous papillomas of external auditory canal.
Malignant transformation of external ear papilloma have been reported.
These are usually solitary lesions. The tumour has a low risk of bony destruction. It grows slowly and can cause a mechanical obstruction of the external auditory canal. The lesion can cause pressure necrosis of the adjacent bone and deafness.
Histologically, the tumour is covered by stratified squamous. They are characterized by papillomatosis , hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, acanthosis, infrequent mitosis and rare nuclear atypia. Squamous cells with clear cytoplasm, dense dark nuclei and occasionally bi-nuclei are called koilocytic cells, which indicate an infection of the cells by HPV.
External ear canal papillomas should be distinguished from other skin lesions including an irritated seborrheic keratosis , carcinoma in situ and invasive SCC , cholesteatoma , skin appendage, and/or other soft tissue neoplasms. However, unlike these lesions, in papillomas there is no glandular pattern, and the cytomorphologic features seen in adenomas. Immunohistochemistry for epithelial markers, such as cytokeratin can highlight a papilloma, rather than a neuroma, since the latter is negative for cytokeratin but is positive for S100 protein.
The occurrence of middle ear squamous papilloma is rare. It is usually associated with sinonasal pathology.